- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记3.4.3 Monopolistic Competition
Characteristics of Monopolistic Markets
- The characteristics of monopolistic competition are as follows
- There are a large number of small firms: each one is relatively small and can act independently of the market
- There is low barriers to entry & exit from the industry: firms can start-up or leave the industry with relative ease which increases the level of competition
- The products are slightly differentiated: this structure exists as consumers have different desires e.g. two nail bars differentiate their product through express or pampered service. Some consumers want an express service & others want to linger. A relatively homogenous product has now been differentiated
- There is a low degree of market power & some price setting ability
Profit Maximising Equilibrium in the Short & Long-run
- In order to maximise profit, firms in monopolistic competition produce up to the level of output where marginal cost = marginal revenue (MC=MR)
- The firm does have some market power and is able to influence the price & quantity
- The firm is a price maker
- This is due to the fact that they have a differentiated product that is desirable by certain consumers
- The firm is a price maker
- The firm can make supernormal profit in the short-run
- In the long-run, the firm will return to a long-run equilibrium position in which they make normal profit
- This is due to inability to defend against new competitors who enter the market & copy the products of existing sellers
- Firms will attempt to find new ways to differentiate their product to prolong the period of supernormal profit e.g. a barber shop may add in a pool table & beer fridge for their customers to enjoy thus making them different from the competition (for a period of time)
Monopolistic Competition Diagrams
Short-run Profit Maximisation
- Firms in monopolistic competition are able to make supernormal profit in the short-run
- The AR curve is the demand curve of the firm & it is downward sloping
- The firm has some market power due to the level of product differentiation that exists
- To sell an additional unit of output, the firm will have to decrease its price
- The marginal revenue (MR) curve will fall twice as quickly as the AR
- The firm has some market power due to the level of product differentiation that exists
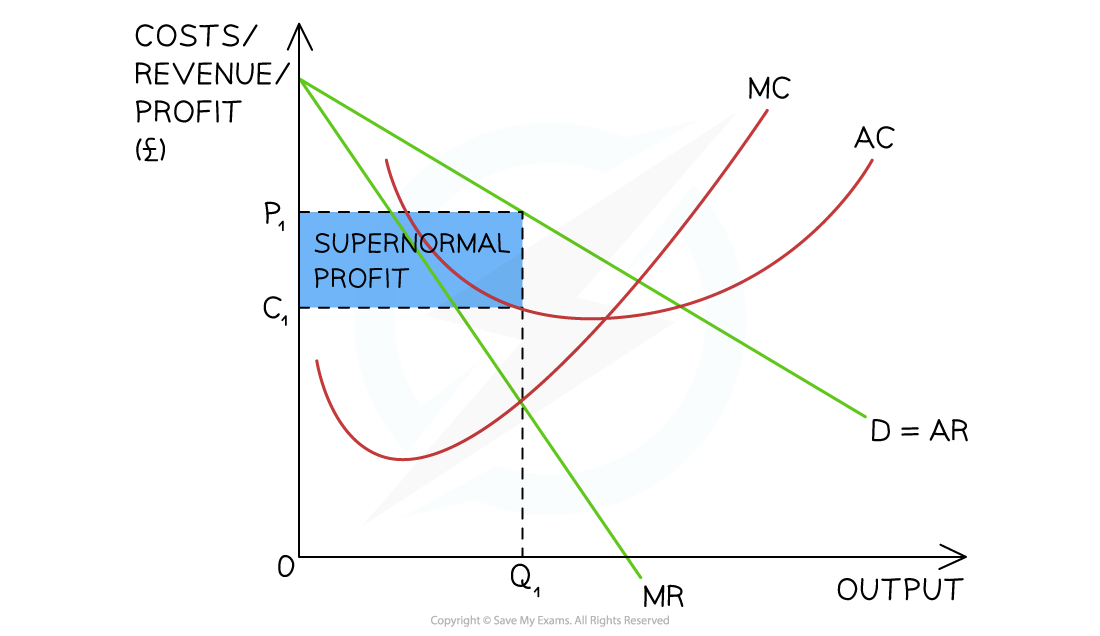
A diagram illustrating a monopolistically competitive firm making supernormal profit in the short-run as the AR > AC at the profit maximisation level of output (Q1)
Diagram Analysis
- The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where MC = MR (Q1)
- At this level the AR (P1) > AC (C1)
- The firm is making supernormal profit
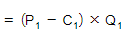
Short-run Losses
- Firms in monopolistic competition are able to make losses in the short-run
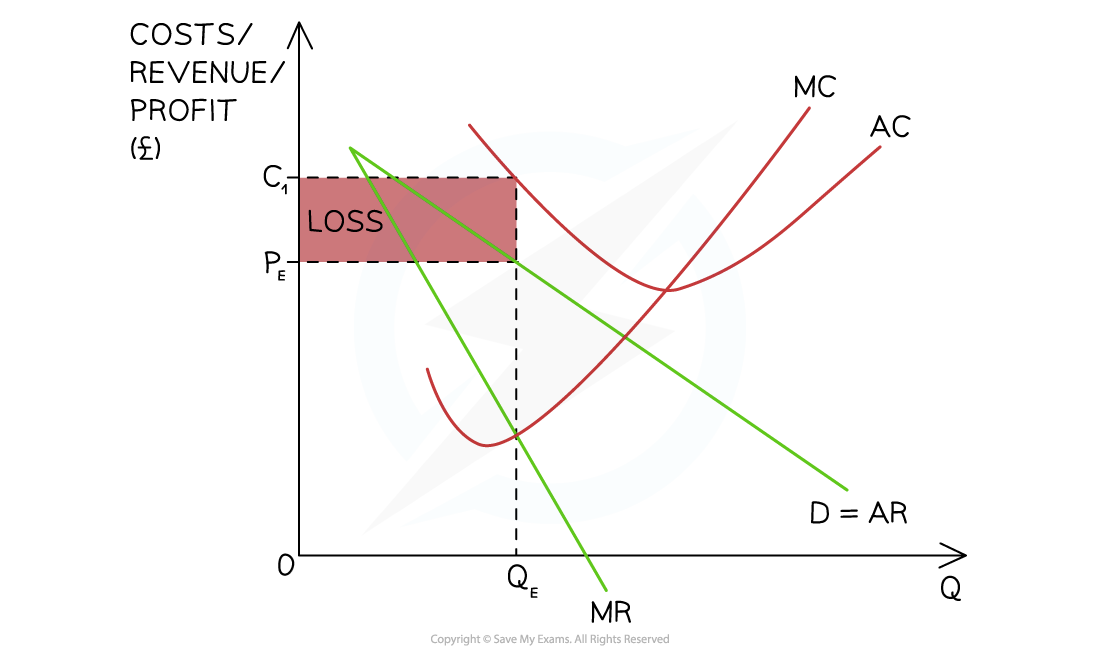
A diagram illustrating a monopolistically competitive firm making losses in the short-run as the AR (PE ) < AC at the profit maximisation level of output (QE)
Diagram Analysis
- The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where MC = MR (QE)
- At this level of output, the AR (PE) < AC (C1)
- The firm's loss is
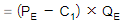
Moving From Short-run Profit/Loss to the Long-run Equilibrium
From Supernormal to Normal Profit
- If firms in monopolistic competition make supernormal profit in the short-run, new entrants are attracted to the industry & the number of sellers increases
- They are incentivised by the opportunity to make supernormal profit
- There are low barriers to entry
- It is easy to join the industry
- Supernormal profit will be eroded & the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
From Losses to Normal Profit
- If firms in monopolistic competition make losses in the short-run, some will shut down
- The shut down rule will determine which firms shut down
- There are low barriers to exit, so it is easy to leave the industry
- For the remaining firms, losses will be eliminated & the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
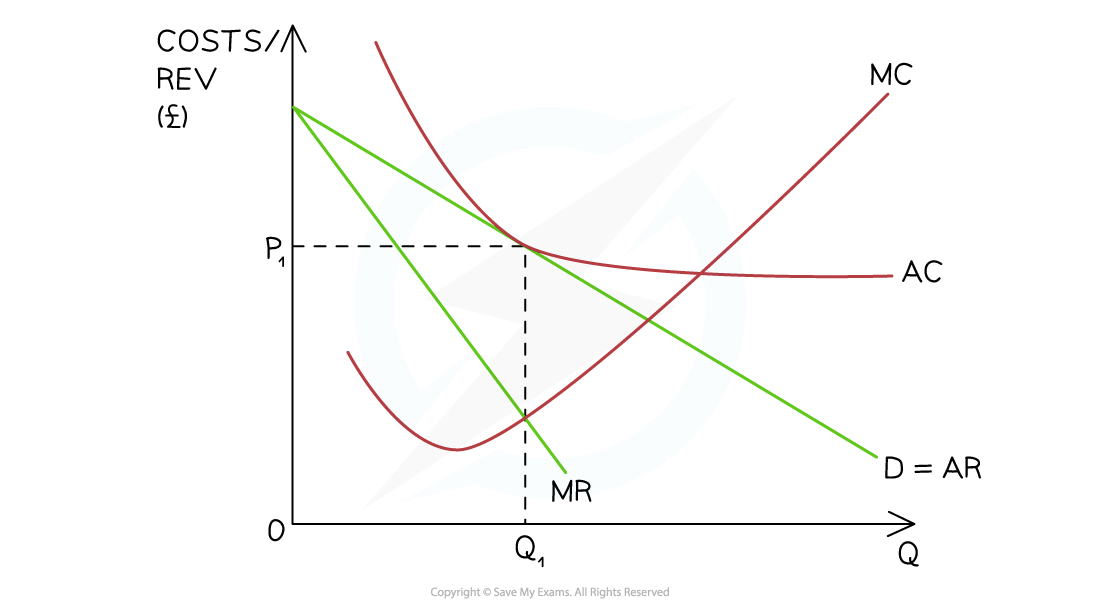

A diagram illustrating the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolistically competitive firm which is making normal profit. AR (P1) = AC at the profit maximisation level of output (Q1)
Diagram Analysis
- The firm is initially producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
- At this level of output P1 = AC & the firm is making normal profit
- In the long-run, firms in monopolistic competition always make normal profit
- Firms making a loss leave the industry
- Firms making supernormal profit see it slowly eradicated as new firms join the industry
转载自savemyexams
站内搜索
竞赛真题免费下载(点击下载)
在线登记
最新发布
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1





