- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记2.5.1 Causes of Growth
Causes of Economic Growth
- Economic growth can occur in the short-run or long-run and each is explained differently
Short-run Economic Growth
- Changes to any of the components of aggregate demand (AD) will cause short-run economic growth to occur
- This is illustrated on an AD/AS diagram by a rightward shift in AD
- It can also be illustrated by using the production possibilities frontier model by moving from a point inside the curve to a point closer to the curve
1. Short-run Economic Growth on AD/AS Diagram
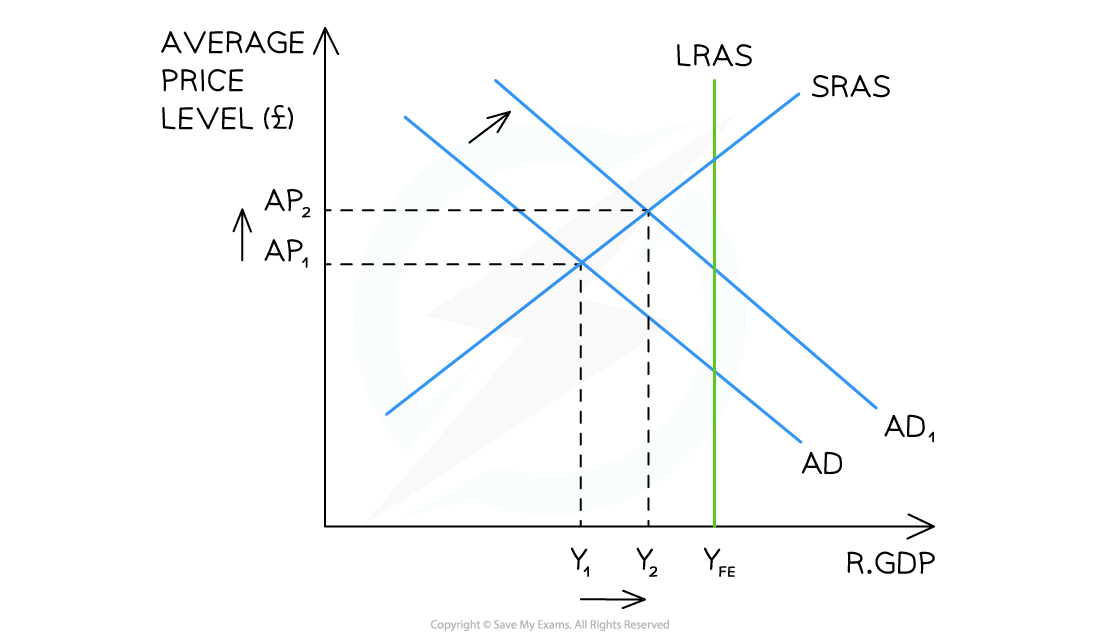
A diagram illustrating short-run economic growth through a shift of aggregate demand from AD→AD1
Diagram Analysis
- An increase in consumption, investment, government spending or net exports has caused a shift in AD from AD→AD1
- The current real output has increased from Y1→Y2 which represents an increase in real GDP
- An increase in real GDP = economic growth
- This short-run growth has led to an increase in average prices from AP1→AP2
2. Short-run Economic Growth on Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)

A diagram illustrating short-run economic growth on a production possibilities frontier (PPF) model
Diagram Analysis
- An increase in production has caused a shift in production combinations from X→Y
- The current real output has increased moving closer to the maximum possible output of the economy
- This represents an increase in real GDP
- An increase in real GDP = economic growth
Long-run Economic Growth
- Long-run economic growth is caused by any improvements to the quality or quantity of the factors of production
- These factors include all of the determinants of long-run aggregate supply
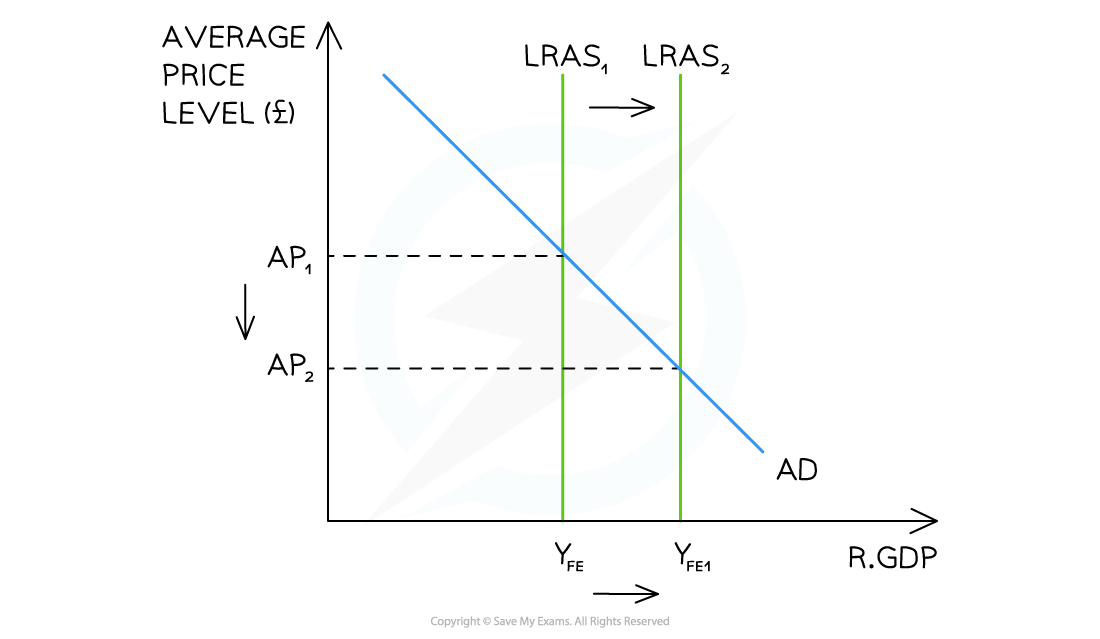
A diagram illustrating long-run economic growth through an increase in the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) of the economy
Diagram Analysis
- A change to the quantity/quality of the factors of production has increased potential output of the economy from YFE→YFE1
- E.g. More rigorous competition policy creates a higher number of firms in each industry leading to greater aggregate supply in the economy
- This shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right LRAS1→LRAS2 resulting in economic growth
- E.g. More rigorous competition policy creates a higher number of firms in each industry leading to greater aggregate supply in the economy
- The final impact on price levels depends on the shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve (Keynesian or Classical)
Actual & Potential Growth
- Actual economic growth occurs when there is an increase in the quantity of goods/services produced in an economy in a given period of time
- This is often measured by the percentage change in real gross domestic product (GDP)
- Potential growth is the increase in the productive potential of an economy as demonstrated by a shift outward of the production possibilities frontier (PPF) or the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve
- At any given point in time, the actual economic growth may be less than the potential growth available to the economy
International Trade & Export-led Economic Growth
- International trade is an important source of income for many countries
- Export-led economic growth refers to growth that occurs as a result of an increase in the sale of goods/services to foreign countries
- Net exports is a component of aggregate demand (AD)
- For many developing countries, the exports represent a high percentage of the annual AD and gross domestic product (GDP)
- When the value of the exports rise, the real GDP rises significantly - and vice versa
- E.g. China experienced significant export-led economic growth from 1988 to the global financial crisis of 2008
转载自savemyexams
站内搜索
竞赛真题免费下载(点击下载)
在线登记
最新发布
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1





