- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: SL复习笔记8.3.1 Acid Deposition
Acid Deposition
What is acid deposition?
- Rain is naturally acidic because of dissolved CO2 which forms carbonic acid
H2O (l) + CO2 (g) ⇌ H2CO3 (aq)
- Carbonic acid is a weak acid and dissociates in the following equilibrium reaction giving a pH of 5.6
H2CO3 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
- For that reason acid rain is defined as rain with a pH of below 5.6
- Acid deposition includes all processes by which acidic components leave the atmosphere
- This could be gases or precipitates
- There are two types of deposition: wet acid deposition and dry acid deposition
- Wet acid deposition refers to rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog, mist and dew
- Dry acid deposition refers to acidic particles and gases that fall to the ground as dust and smoke
- Acid deposition is formed when nitrogen or sulfur oxides dissolve in water to form HNO3, HNO2, H2SO4 and H2SO3
Acid Deposition Equations
Formation of sulfur based acids
- Fossil fuels are often contaminated with small amounts of sulfur impurities
- When these contaminated fossil fuels are combusted, the sulfur in the fuels get oxidised to sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
- Sulfur dioxide may be further oxidised to sulfur trioxide
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3 (g)
- The sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide then dissolve in rainwater droplets to form sulfurous acid and sulfuric acid
SO2(g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
SO3 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq)
- These acids are components of acid rain which has several damaging impacts on the environment
Formation of acid rain by nitrogen oxides
- The temperature in an internal combustion engine can reach over 2000 °C
- Here, nitrogen and oxygen, which at normal temperatures don’t react, combine to form nitrogen monoxide:
N2 (g)+ O2 (g) ⇌ 2NO (g)
- Nitrogen monoxide reacts further forming nitrogen dioxide:
2NO (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g)
- Nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with rain water to form a mixture of nitrous and nitric acids, which contribute to acid rain:
2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO2 (aq) + HNO3 (aq)
- Lightning strikes can also trigger the formation of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxides in air
- Nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with rain water and more oxygen to form nitric acid
4NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)→ 4HNO3 (aq)
- When the clouds rise, the temperature decreases, and the droplets get larger
- When the droplet containing these acids are heavy enough, they will fall down as acid rain
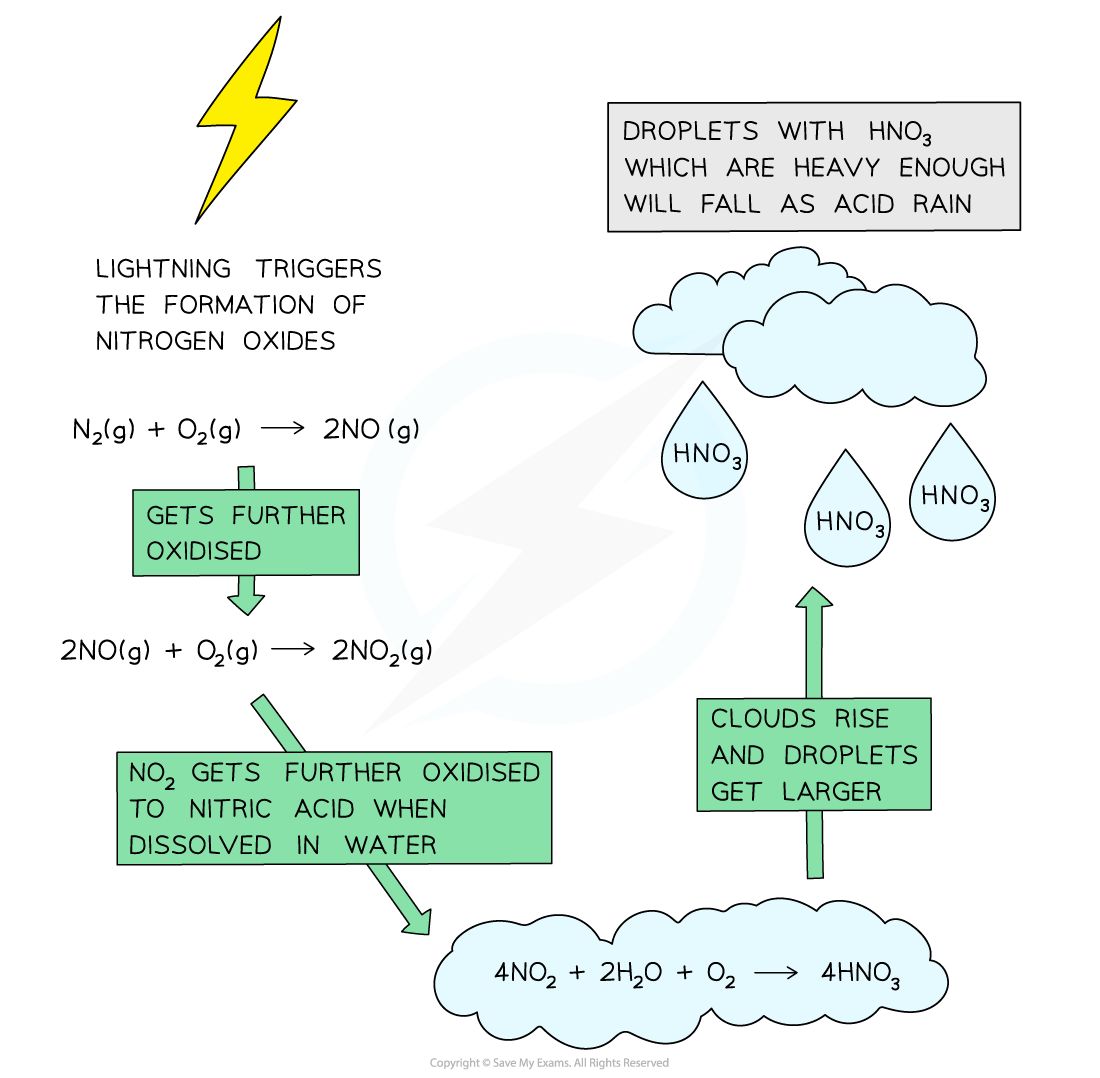
The diagram shows the formation of acid rain by the oxidation of nitrogen dioxide
转载自savemyexams
站内搜索
竞赛真题免费下载(点击下载)
在线登记
最新发布
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1





