- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Maths 复习笔记 3.11.4 Differentiation - Kinematics
Edexcel IGCSE Maths 复习笔记 3.11.4 Differentiation - Kinematics
What is kinematics?
- Kinematics is the analysis of the motion of a particle linking the three vector quantities displacement, velocity and acceleration – see below
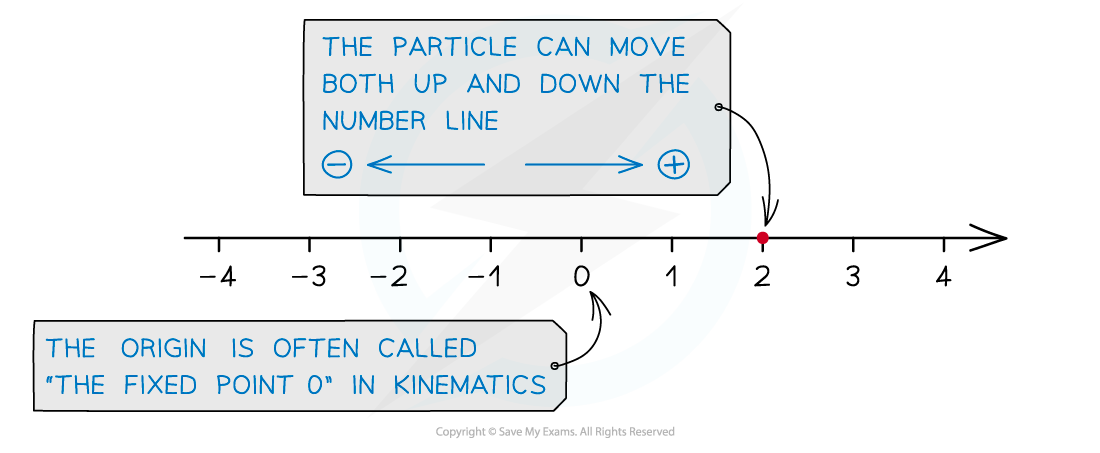
- Motion is in a straight line – think of the particle as moving along a number line
- The number line has a fixed point O (the origin)
- The number line has both negative and positive values
- The particle can move in both directions along the number line
- Note that in kinematics, a particle is an object – it could be a football, a car, a train - anything that has motion. A particle is modelled as taking up a single point in space
- Ensure you are familiar with Differentiation - Basics andDifferentiation – Turning Points before continuing
- It may be wise to look at Differentiation – Problem Solving too
What is displacement; isn’t it the same as distance?
- Displacement is a vector quantity, so it can be negative
- Distance is always positive
- Displacement is measured from the fixed point O
- The letter s is used for displacement
- It is usually measured in metres (m)
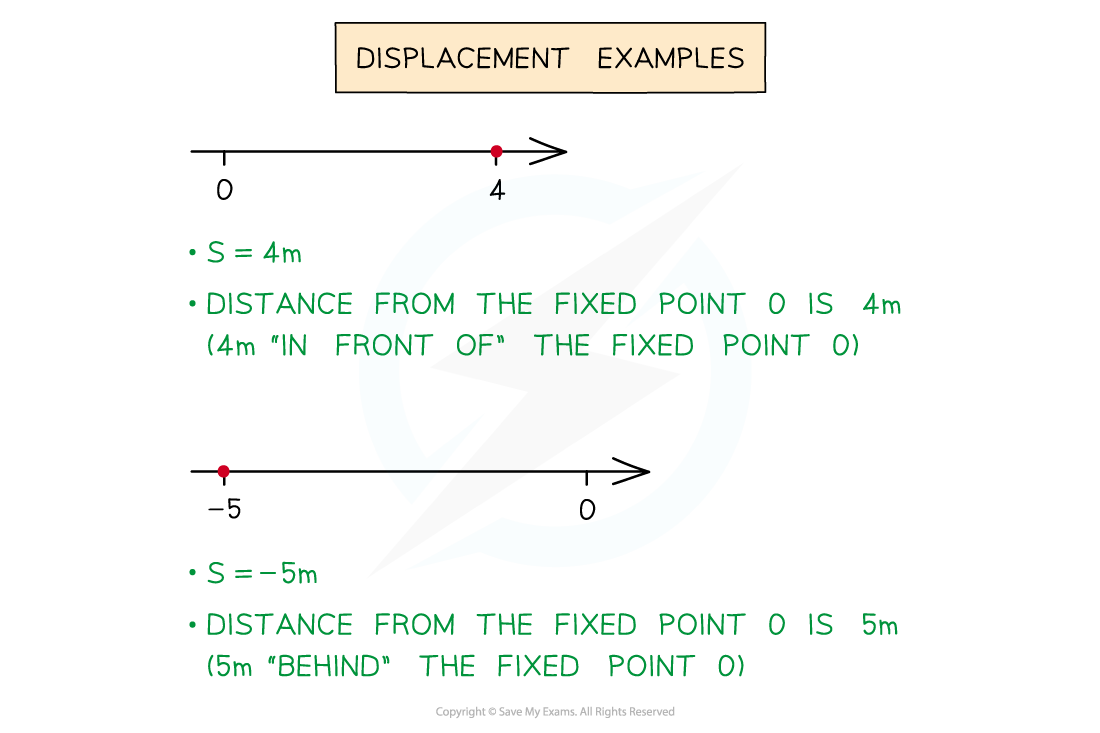
- If s = 4 then the distance from the origin is 4 m and the particle is 4 m “in front of” the origin
- If s =-5 then the distance from the origin is 5 m and the particle is 5 m “behind” the origin
- The + or - indicates the particle’s position relative to the origin
- Displacement is a function of time, t, where time is usually measured in seconds
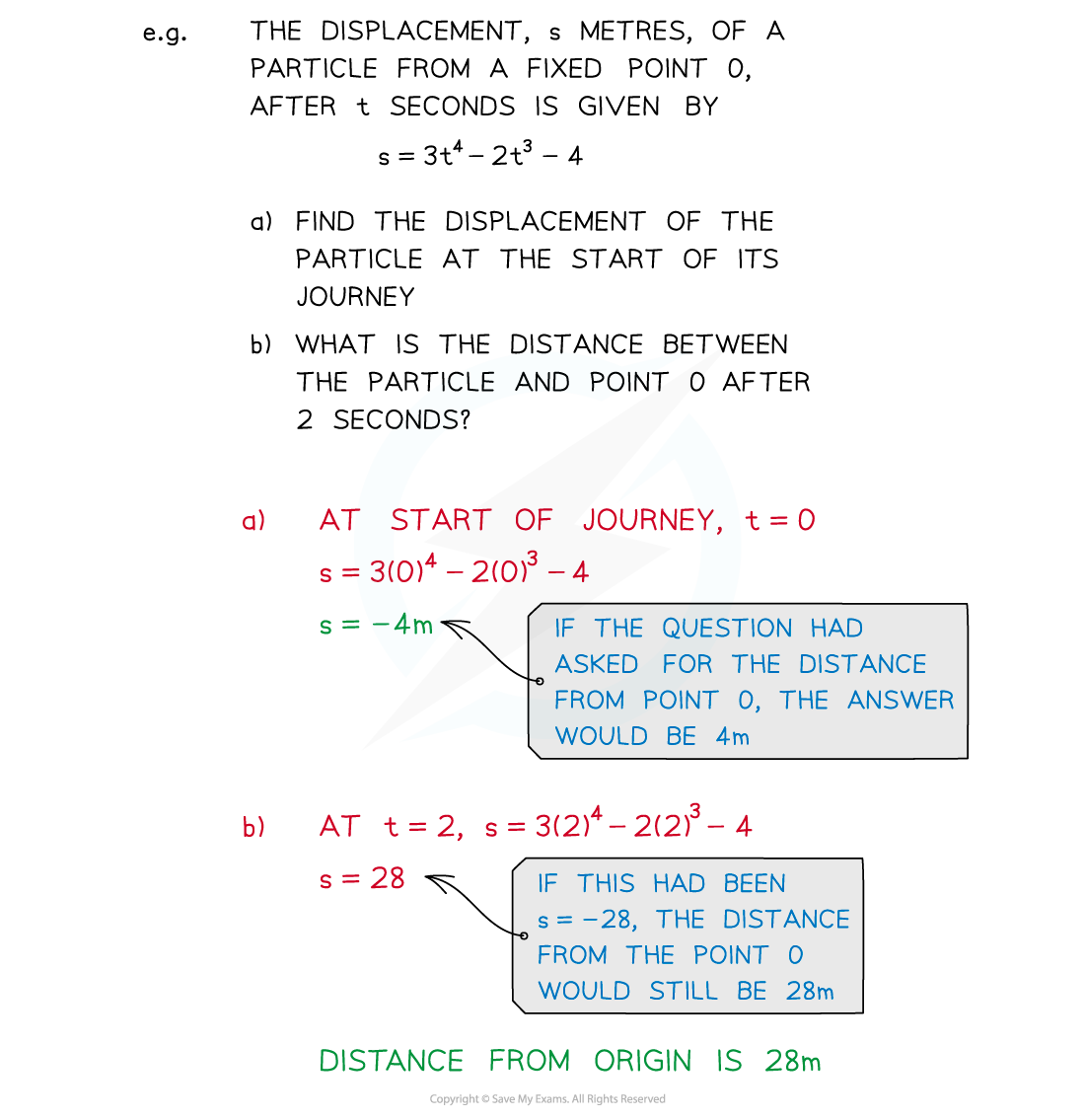
- eg. s = 3t3 - 2t + 1
At time t = 0, s = 1At time t = 2, s = 21
- eg. s = 3t3 - 2t + 1
What is velocity; isn’t it the same as speed?
- Velocity is a vector quantity, so it can be negative
- Speed is always positive
- The letter v is used for velocity
- It is usually measured in metres per second (m/s)
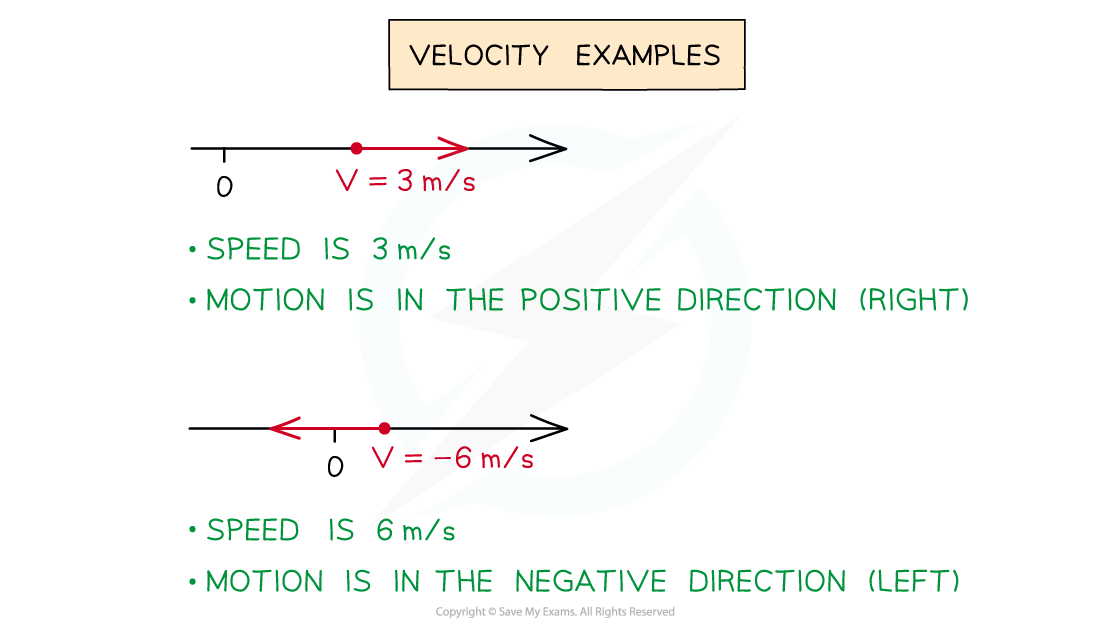
- If v = 3 then the speed of the particle is 3 m/s and it is moving in the positive direction
- If v = -6 then the speed of the particle is 5 m/s and it is moving in the negative direction
- The + or - indicates the particle’s direction of motion
- Velocity is a function of time, t, and is the rate of change of displacement
- To find v, differentiate s, ie. v = ds/dt
If s = t3 - 2t2then v = ds/dt = 3t2 – 4t
- To find v, differentiate s, ie. v = ds/dt
- If velocity is zero then the particle is stationary (not moving)
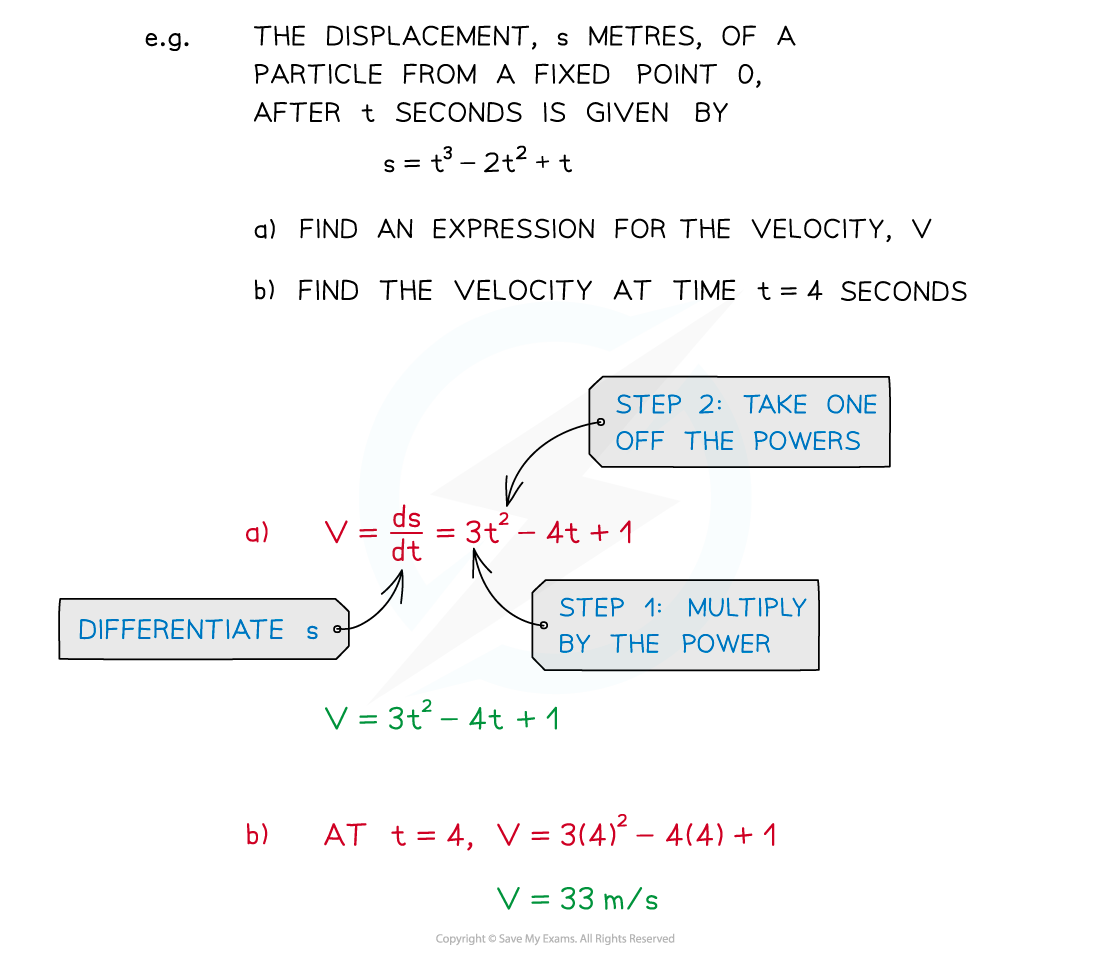
What is acceleration?
- Acceleration is a vector quantity, so it can be negative
- The magnitude of acceleration is always positive
- The letter a is used for acceleration
- It is usually measured in metres per square second (m/s2)
- If a = 1 then the magnitude of acceleration is 1 m/s2 and the particle is accelerating (velocity increasing)
- If a = -6 then the magnitude of acceleration is 6 m/s2 and the particle is decelerating (velocity decreasing)
- The + or - indicates whether the particle is accelerating or decelerating
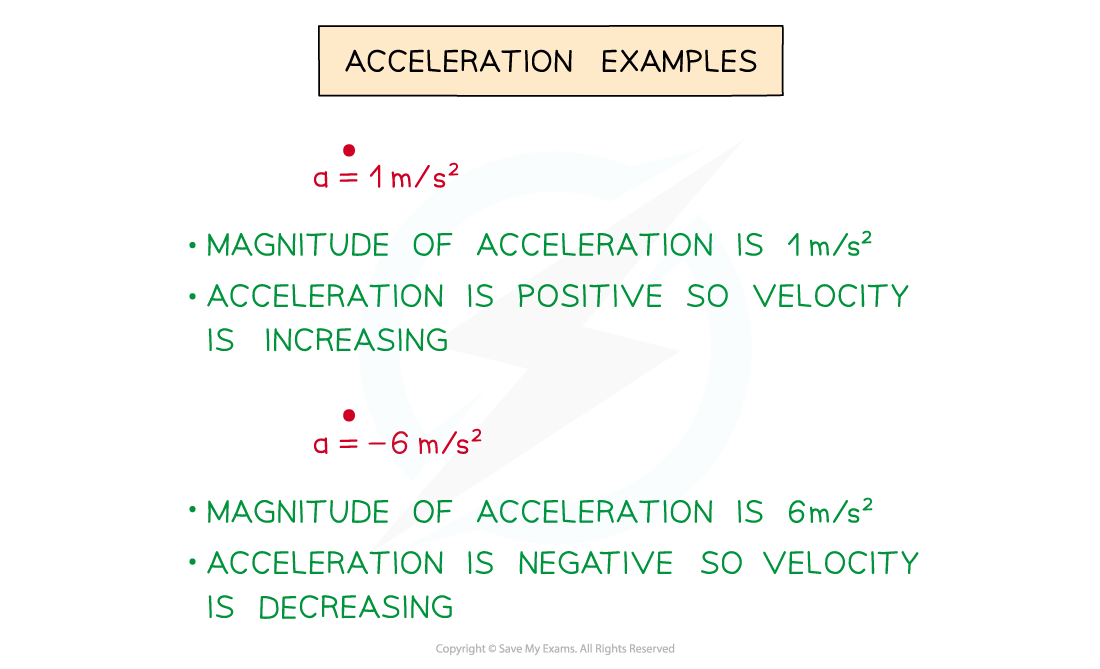
- Acceleration is a function of time, t, and is the rate of change of velocity
- To find a, differentiate v, ie. a = dv/dt
If v = 3t2 – 4tthen a = dv/dt = 6t - 4
- To find a, differentiate v, ie. a = dv/dt
- If acceleration is zero then the particle is moving at a constant velocity

How do I solve kinematics problems?
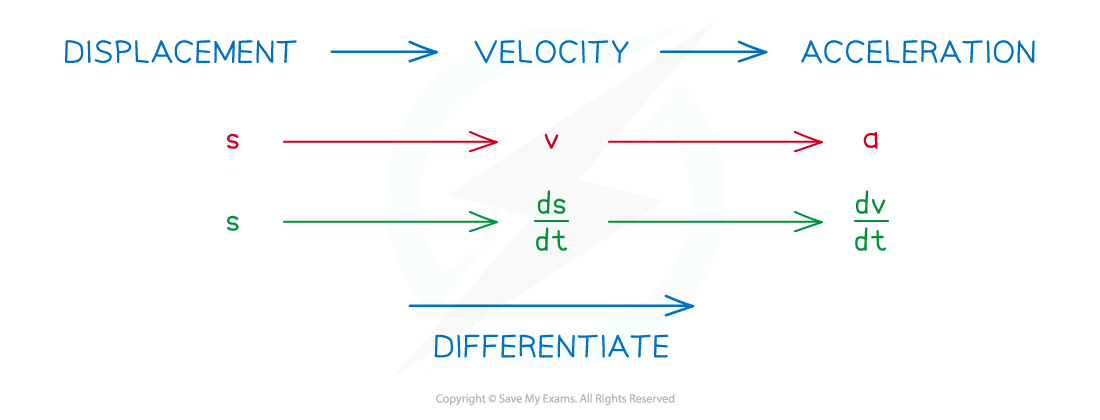
- Be clear about how the three quantities are related through differentiation
- v = ds/dt
- a = dv/dt
- There are some key phrases to look out for
- “... initial ...” / “... initially ...”
This means at the start, so when t = 0
- “... at rest ...”
This means the particle is stationaryso v = 0
- “... instantaneously ...”This means at some point in time, for some value of t
- “... initial ...” / “... initially ...”
- For example,“Find the value(s)s of t for which the particle is instantaneously at rest”
- means find the time(s) when v = 0,
- ie. solve the equation v = 0
Exam Tip
Displacement, velocity and acceleration can all be negative whereas distance, speed and magnitude of acceleration are always positive.
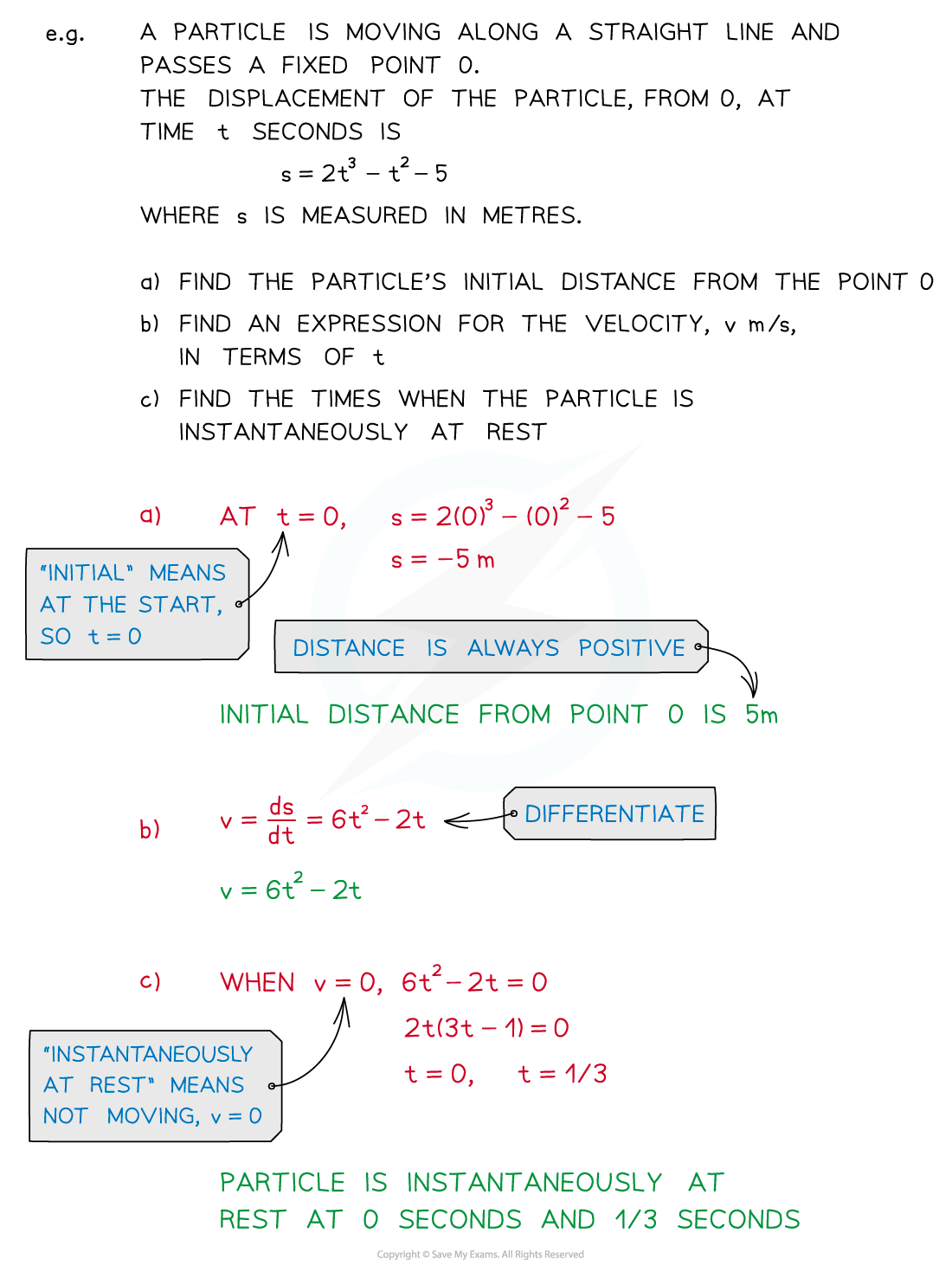
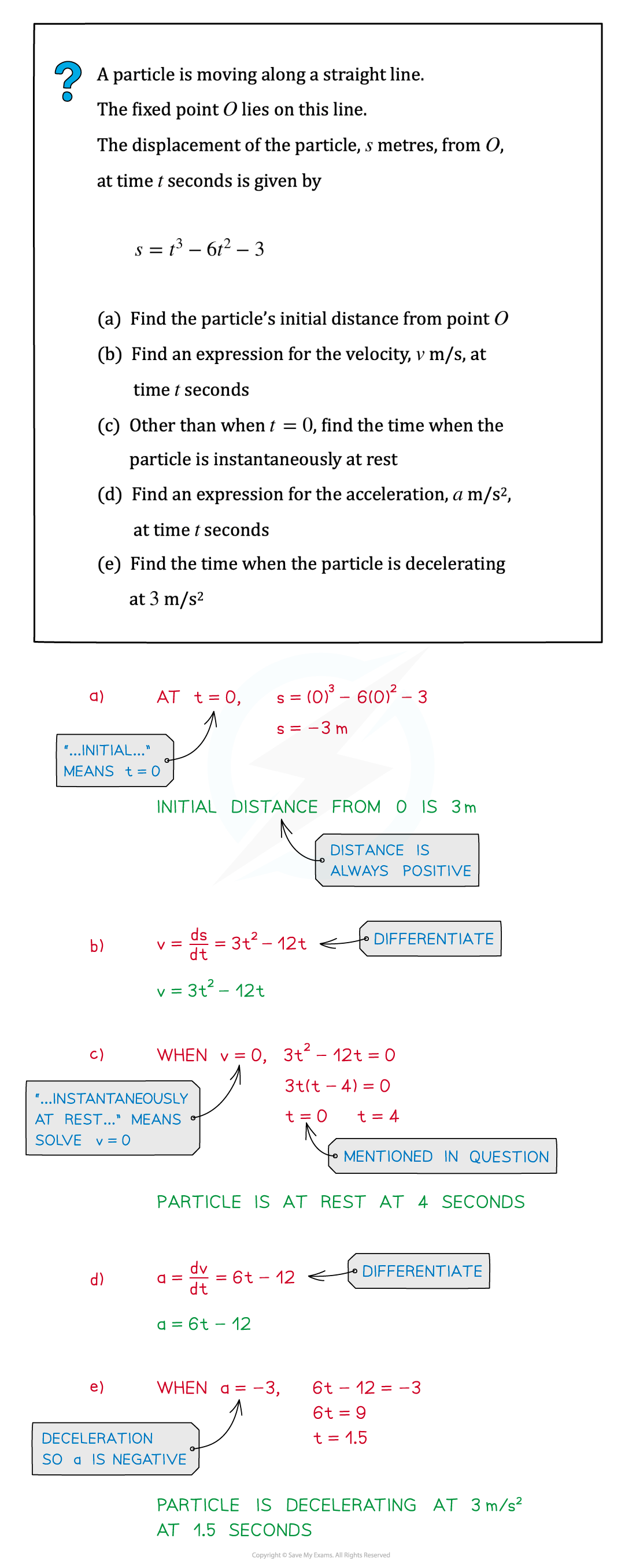
Worked Example
转载自savemyexam
站内搜索
竞赛真题免费下载(点击下载)
在线登记
最新发布
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1





